Understanding the Fire Triangle: Essential Knowledge for UK Fire Safety Compliance
11th Dec 2024

Introduction to the Fire Triangle
The fire triangle is a fundamental concept in fire safety and prevention, providing a simple model for understanding the necessary ingredients for fires: heat, fuel, and oxygen. This model illustrates how these three elements interact to sustain a fire and how removing any one of them can extinguish it. By understanding the fire triangle, individuals and businesses can enhance their emergency response and implement robust fire safety measures.
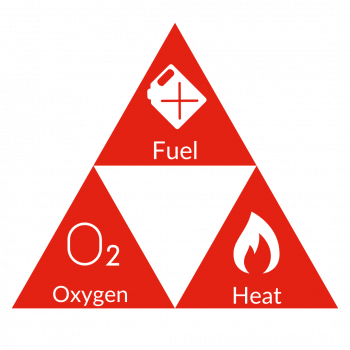
The Three Elements of the Fire Triangle
The fire triangle consists of three essential elements: heat, fuel, and oxygen. Each plays a critical role in sustaining a fire, and their interaction is the key to understanding fire dynamics.
- Heat is the energy source that raises the temperature of the fuel to its ignition point. Heat, as an element of the fire triangle, can originate from various sources such as open flames, electrical sparks, or hot surfaces. It is the catalyst that ignites the fuel, setting off the chain reaction that sustains a fire. Without sufficient heat, even the most flammable materials will not ignite, underscoring the importance of temperature control in fire prevention strategies.
- Fuel provides the material that combusts, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. Fuel, the second element, can be any combustible material that supports a fire. This includes solids like wood, liquids like petrol, and gases like methane. By managing and controlling fuel sources, the risk of fire ignition can be significantly reduced. This element is critical in fire risk assessments, where identifying and mitigating potential fuel sources is a primary focus.
- Oxygen supports combustion by maintaining the chemical reaction that occurs during a fire. Did you know there needs to be at least 16% Oxygen in the air to start combustion.
As such, understanding each element of the fire triangle and their interactions is fundamental to effective fire management.
Controlling Heat
Controlling heat is an essential aspect of fire suppression, with cooling being one of the most effective techniques. Water is a primary suppressant used due to its heat absorption properties, effectively lowering the temperature of the burning material and preventing the fire from escalating. Effective cooling is essential in preventing a fire from escalating, with water being a primary suppressant due to its heat absorption properties.
In addition to water, other fire suppressants such as foam works by absorbing heat, interrupting the chemical reaction, or creating a barrier between the fuel and oxygen.
Fuel Sources
Common fuel sources in commercial and industrial settings include paper, textiles, oils, and gases. Each of these fuels has specific management requirements to prevent accidental ignition. By understanding these requirements and implementing appropriate storage and handling procedures, businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood of fire incidents.
Proper storage and handling of combustible materials are critical in mitigating fire hazards. By ensuring that all flammable materials are stored safely and away from potential ignition sources, the risk of accidental fires can be significantly reduced. This involves adhering to guidelines and regulations that dictate safe storage practices for various types of fuels.
Reducing Oxygen Supply
Reducing the oxygen supply to a fire is another effective method of fire suppression. Smothering techniques, such as using fire blankets or extinguishers, are commonly employed to cut off the oxygen supply, thereby extinguishing the fire.
Oxygen reduction methods vary in effectiveness depending on the fire situation. For instance, while a fire blanket may be sufficient for a small, contained fire, larger fires may require the use of specialised extinguishers or suppression systems that can deploy oxygen-displacing agents like carbon dioxide or inert gases.
The principles behind oxygen reduction are rooted in the chemical requirements for combustion. By eliminating the oxygen component of the fire triangle, the combustion process is interrupted, and the fire is unable to sustain itself. This technique is particularly useful in confined spaces where ventilation is limited, and rapid oxygen displacement can effectively halt combustion.
Implementing Fire Safety Protocols in Compliance with UK Regulations
Implementing fire safety protocols in compliance with UK regulations is essential for ensuring both safety and legal adherence. UK fire safety regulations, such as the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005, provide guidelines on the measures that must be taken to prevent fires and protect people in the event of a fire. Compliance with UK fire safety regulations involve integrating comprehensive understanding of the fire triangle into safety protocols.
How Red Box Fire Control Can Assist
Red Box Fire Control offers a range of services designed to assist businesses in managing fire safety components effectively. With extensive expertise and a commitment to safety, Red Box Fire Control ensures comprehensive fire management solutions. Our services include fire risk assessments, fire safety training, and the provision of high-quality fire safety equipment.
By partnering with Red Box Fire Control, businesses can benefit from our extensive knowledge and experience in the fire safety industry. We are committed to delivering quality-assured products and services that meet the highest standards of safety and compliance, providing peace of mind to our clients.

